Sugar beet vs sugar cane: Financial aspects in the global sugar market
All Regarding Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane: Which One Uses Greater Advantages and Utilizes?
The comparison in between sugar beet and sugar cane presents a nuanced exploration of their respective benefits and applications. Each plant has unique nutritional profiles and expanding conditions that influence their usage in numerous sectors. As consumer preferences change in the direction of much healthier choices, the relevance of these 2 sources of sugar comes to be increasingly substantial. Recognizing their distinctions might reveal insights right into which might eventually offer much better in an altering market landscape. What factors will form this recurring dispute?
Summary of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane
Sugar beet and sugar cane are 2 key sources of sugar, each with distinctive features and benefits. Sugar beet, a root plant mainly expanded in temperate climates, is known for its high sucrose content, which can range from 15% to 20%. This crop is typically processed into granulated sugar, molasses, and various other byproducts. Its growing permits a much shorter growing period and much less dependence on tropical climates.
In contrast, sugar cane thrives in warmer, tropical areas and is frequently concerned for its coarse stalks, which can yield 10% to 15% sucrose. The processing of sugar cane not only creates sugar however likewise leads to products like rum and ethanol, making it versatile. Both plants add considerably to the worldwide sugar market, with their one-of-a-kind growing conditions and handling methods affecting their farming and financial value. Inevitably, the option in between sugar beet and sugar cane often relies on local environments and market needs.
Nutritional Profiles: Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane
The nutritional profiles of sugar beet and sugar cane reveal substantial differences in their nutrient make-ups. Sugar beet tends to provide a higher focus of minerals and vitamins, while sugar cane mainly supplies energy in the kind of carbohydrates. In addition, the glycemic index of these 2 resources differs, affecting their impacts on blood glucose degrees.
Nutrient Composition Contrast
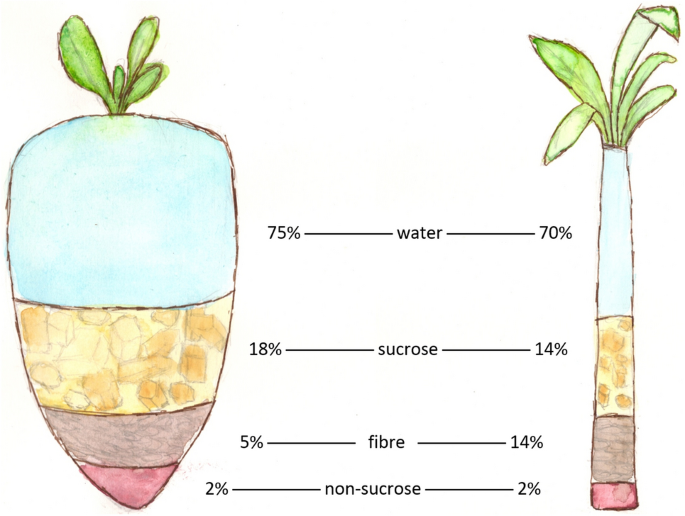
When contrasting the nutrient structure of sugar beet and sugar cane, distinctive differences emerge that can affect nutritional selections. Sugar beets are known for their greater fiber content, providing approximately 2 grams of fiber per 100 grams, while sugar cane has marginal fiber (Sugar beet vs sugar cane). Relating to vitamins, sugar beets use a variety of B vitamins, specifically folate, which supports mobile wellness, whereas sugar cane contains fewer vitamins overall. In addition, sugar beets flaunt a higher mineral web content, consisting of potassium and magnesium, important for various physical features. Sugar cane largely offers carbs, particularly sucrose, yet lacks the nutrient thickness located in sugar beets. These differences highlight the dietary advantages of sugar beets contrasted to sugar cane in a balanced diet plan

Glycemic Index Differences
Just how do sugar beets and sugar cane vary in their glycemic index, and what implications does this have for individuals monitoring their blood sugar level levels? Sugar beetroots generally have a reduced glycemic index (GI) contrasted to sugar cane, which implies they trigger a slower and extra steady increase in blood sugar degrees. This distinction is specifically important for individuals with diabetes or those concerned regarding blood sugar level monitoring. A reduced GI food can aid keep steadier power degrees and decrease the threat of insulin spikes. While both sources are mostly composed of sucrose, the varying fiber and nutrient material in sugar beetroots might add to their reduced GI, making them a potentially much better alternative for health-conscious customers.
Expanding Problems and Geographic Circulation
Although both sugar beet and sugar cane act as crucial resources of sugar, their expanding problems and geographical circulation vary substantially. Sugar cane grows in exotic and subtropical environments, calling for warm temperature levels, abundant sunshine, and significant rains. It is generally grown in countries such as Brazil, India, and China, where these environmental elements are excellent. Sugar beet vs sugar cane. In contrast, sugar beet prefers temperate environments, prospering in cooler areas with well-drained soil. Significant manufacturers of sugar beet consist of the United States, Russia, and numerous European countries, where the growing period lines up with cooler temperature levels
The distinctions in climate requirements bring about differing growing practices; sugar cane is frequently grown as a perennial crop, while sugar beet is generally planted each year. This geographical difference not only affects regional farming economies however additionally shapes regional practices connected to sugar production and processing. Recognizing these aspects is necessary for examining the benefits and applications of each resource.
Environmental Effect of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Production
While both sugar beet and sugar cane add considerably to global sugar manufacturing, their environmental impacts differ substantially. Sugar cane farming commonly necessitates big stretches of land and water, resulting in logging and environment loss in some regions. Additionally, the usage of plant foods and pesticides in sugar cane farming can lead to dirt deterioration and water pollution. Alternatively, sugar beet is usually expanded in cooler climates and needs much less water, which may decrease the stress on local water resources. Nonetheless, intensive farming methods connected with sugar beet can additionally result in soil erosion and nutrient deficiency. The processing of both crops generates waste, however sugar cane YOURURL.com has a greater possibility for by-products, such as bioenergy, which can reduce some environmental effects. Ultimately, the sustainability of each crop mainly relies on farming techniques and regional management techniques used throughout the manufacturing cycle.
Handling Approaches and Efficiency
Processing techniques for sugar beet and sugar cane vary considerably, influencing total performance and return. Sugar beetroots undergo a procedure that consists of washing, slicing, and drawing out juice with diffusion or pushing. The juice is after that detoxified, concentrated, and taken shape, causing granulated sugar. This approach is normally reliable, with a high sugar extraction rate.
On the other hand, sugar cane processing involves squashing the cane to extract juice, followed by explanation and dissipation. The juice is after that steamed to create sugar crystals. While both approaches are reliable, sugar cane handling YOURURL.com can be a lot more labor-intensive and lengthy because of the larger scale of procedures and the need for more comprehensive equipment.
Additionally, sugar beet processing often results in a greater sugar material per heap contrasted to sugar cane, making it a much more efficient option in particular areas. On the whole, the selection of handling method influences not just the yield but additionally the economic practicality of sugar manufacturing.
Applications in the Food Market
In the food industry, sugar beet and sugar cane offer distinctive roles in sugar production. Each resource provides unique features that influence their cooking applications, from baked products to beverages. Recognizing these differences can assist producers and cooks in selecting one of the most suitable ingredient for their demands.
Sweetener Manufacturing Distinctions
Both sugar beet and sugar cane serve as necessary resources for sweetener manufacturing, their applications in the food sector differ significantly. Sugar cane is mostly related to producing raw sugar and molasses, which are commonly made use of in beverages, confections, and baked goods. Its juice is additionally fermented to create rum. On the other hand, sugar beet is generally processed right into polished sugar, which is favored in the production of granulated sugar and numerous other sugar. The extraction procedure for sugar beet is extra uncomplicated, enabling greater yields of white sugar. In addition, sugar beet's adaptability makes it possible for the creation of alternate sugar, such as beet syrup. These distinctions highlight the distinct roles each source plays in satisfying the diverse requirements of the food market.
Culinary Utilizes Comparison
Culinary applications of sugar beet and sugar cane expose unique choices amongst chefs and food makers. Sugar cane, frequently viewed as the standard sugar, is favored in a selection of products, consisting of syrups, molasses, and drinks like rum. Its natural flavor complements desserts, marinades, and sauces. Alternatively, sugar beet, made use of mostly in granulated sugar kind, is regularly incorporated into baked products, candies, and processed foods. Its neutral flavor account permits it to mix flawlessly into different recipes. In addition, sugar beet is obtaining grip in natural and non-GMO markets, attracting health-conscious consumers. Ultimately, the choice between sugar beet and sugar cane rests on details cooking applications, flavor preferences, and market fads within the food sector.
Health And Wellness Considerations and Consumer Preferences
An expanding variety of customers are significantly knowledgeable about the health effects connected with sugar sources, resulting in an eager interest in the advantages of sugar beet versus sugar cane. Both sugar resources have distinct dietary profiles that may affect customer options. Sugar beets often tend to consist of slightly extra fiber and crucial nutrients, which can interest health-conscious individuals. Alternatively, sugar cane is usually viewed as a more all-natural and less refined choice, possibly drawing in those seeking natural or raw products.
Furthermore, the climbing popularity of alternate sugar has motivated customers to scrutinize standard sugars much more very you could look here closely. Recognition of excessive sugar usage's health and wellness risks, such as excessive weight and diabetic issues, has actually fueled a need for openness concerning the beginnings and handling techniques of sugar. Ultimately, private choices remain to form the debate between sugar beet and sugar cane, mirroring a broader trend in the direction of healthier eating routines and educated consumerism
Regularly Asked Inquiries
What Are the Historical Uses Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
Historically, sugar beet and sugar cane have actually worked as primary resources of sugar. Sugar cane, grown for centuries in exotic areas, provided sweeteners, while sugar beet emerged in Europe during the 18th century, improving regional sugar manufacturing.

Exactly How Do Sugar Beet and Cane Affect Resident Economies?
Sugar beet and sugar cane substantially influence neighborhood economies through job creation, agricultural efficiency, and trade. Their cultivation fosters rural development, sustains neighborhood organizations, and creates tax obligation profits, eventually enhancing neighborhood sustainability and financial strength.
Are There Any Cultural Significance Distinctions In Between Sugar Beet and Cane?
Social value varies between sugar beet and sugar cane. Sugar cane usually stands for tropical heritage and conventional practices, while sugar beet is linked with agricultural technology and automation, showing different local identifications and historical contexts in their manufacturing.
What Are the Main Pests Affecting Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane?
The primary pests influencing sugar beet consist of aphids and root maggots, while sugar cane faces hazards from borers and planthoppers. Both plants need mindful administration to minimize damages and guarantee healthy and balanced yields.
How Do Climate Adjustments Effect Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Farming?
Climate adjustments greatly affect sugar beet and sugar cane farming by altering development problems, shifting pest populations, and influencing water availability. These aspects can decrease returns and affect general farming sustainability in influenced regions.